Role of Technology in Insurance Sector of Morocco
Developing FinTech in Morocco
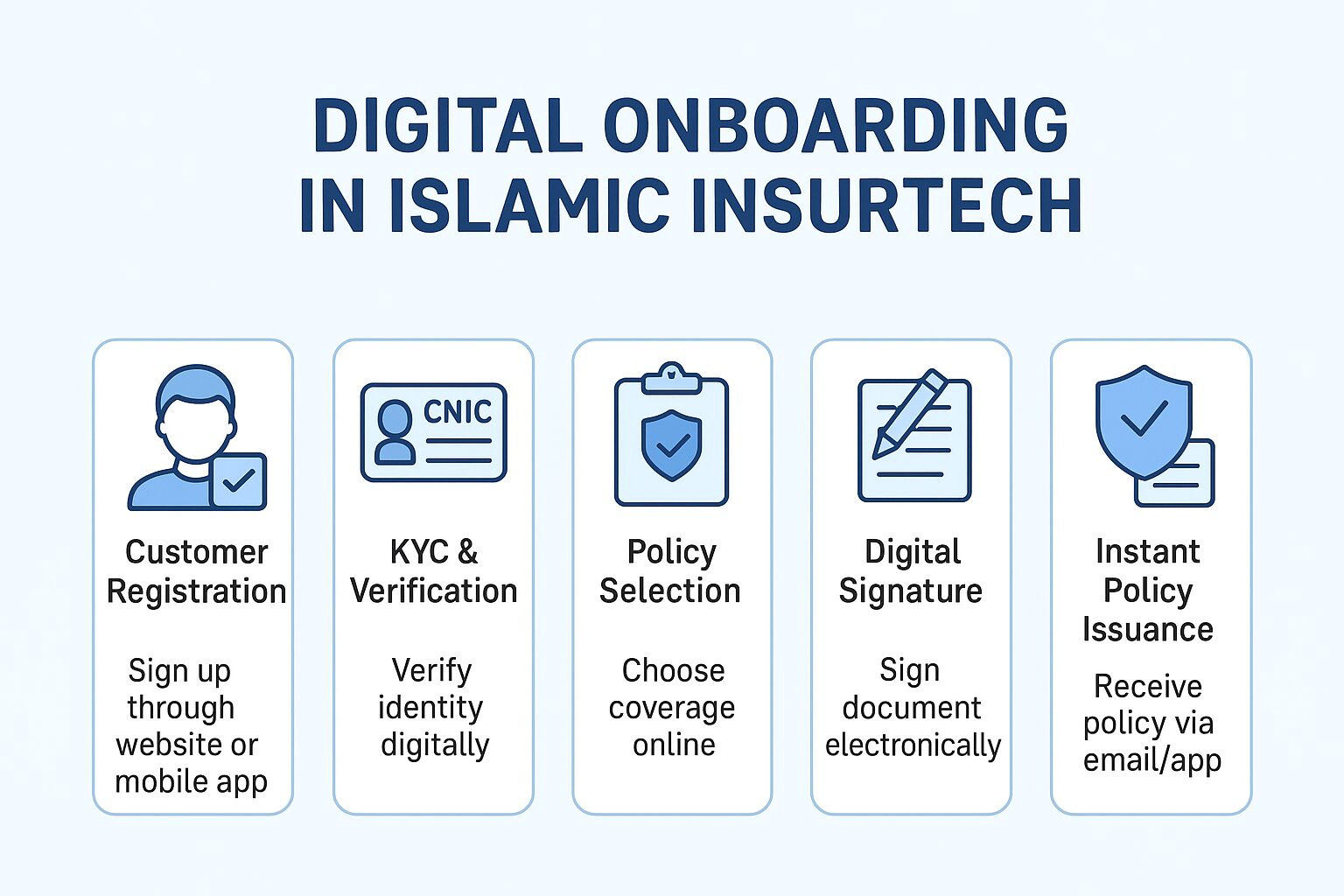
Developing FinTech in Morocco requires further investment in digitization. Affordable high-speed internet, a skilled digital workforce, and digital platforms are essential for boosting FinTech. However, rural-urban digital divides and low financial service penetration pose challenges.

Impact of ICT on Insurance Sector
A study on 48 African nations, including Morocco, between 2004-2014 found that ICT dynamics such as mobile and broadband subscriptions enhance insurance consumption and efficiency (Asongu et al., 2019).
Neobanks and AI-Powered Banking
Neobanks and FinTech companies challenge traditional banks with AI-powered banking solutions, offering automated processes that reduce errors and costs (Anand, 2022).
Cashless Digital Payments
Digital payments minimize transaction risks, increase efficiency, and reduce fraud in loan disbursement and repayment processes (Ray et al., 2018).
Technology in Agricultural Insurance
Rainfall-based insurance models help Moroccan farmers mitigate financial risks. Proportional rainfall insurance compensates based on actual vs. trigger rainfall (Skees et al., 2001).
CRM and Automation in Moroccan Banks
Moroccan banks leverage IT for customer relationship management (CRM), enabling personalized financial services and efficient knowledge management (Youssef et al., 2017).
Automation and AI in Insurance
Automation modernizes financial operations, reducing human errors and biases. AI-driven risk analysis speeds up claim processing and provides fair insurance rates (IBEF, 2021).
Challenges and Future Prospects
Morocco must address financial accessibility, regulatory improvements, and digital infrastructure expansion to fully harness technology’s potential in the insurance sector.
External Resources