Agriculture Insurance in India: A Key Driver for Economic Growth
Agriculture insurance plays a crucial role in the economic development of India, where nearly two-thirds of the population depends on agriculture. The country has 67 insurance providers, including 24 life insurers, 26 general insurers, 5 stand-alone health insurers, and 12 re-insurers.

Regulatory Bodies & Industry Associations
India’s insurance sector is regulated by the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) and the Ministry of Finance. Key industry associations include:
- Life Insurance Council of India
- General Insurance Council of India
- India InsurTech Association
Evolution of Crop Insurance in India
The Indian government has launched several initiatives to mitigate risks faced by farmers due to climate-related disasters. The first crop insurance scheme was introduced in 1972 by the Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC), covering cotton farmers in Gujarat. Over the years, the coverage expanded to include crops like groundnuts, wheat, and potatoes.
Key Milestones in Crop Insurance
- 1972: Comprehensive Crop Insurance Scheme (CCIS) launched.
- 1985: National Agricultural Insurance Scheme (NAIS) introduced for yield protection against drought, floods, and cyclones.
- 2013: Modified National Agricultural Insurance Scheme (MNAIS) included pest and disease coverage.
- 2016: Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) introduced, covering all crops and risks.
Challenges & Future Prospects
Despite being the world’s largest crop insurance program, insuring 25 million farmers, several challenges remain. These include delays in claims settlement and a significant portion of farmers remaining uninsured. The Indian government is piloting a market-based approach under the Modified National Agricultural Insurance Scheme to enhance private sector participation.
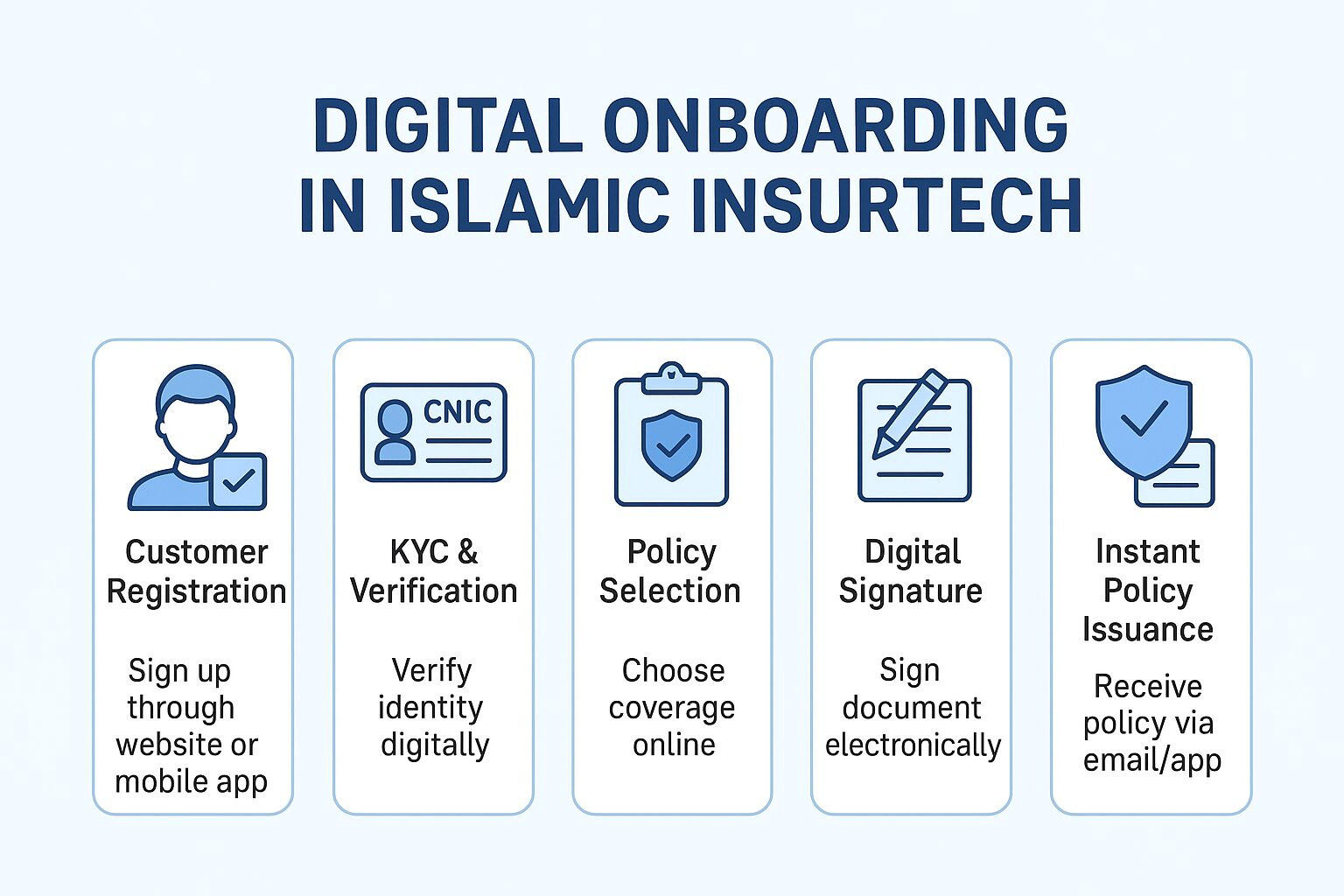
Digital Transformation & InsurTech in India
India’s insurance industry is rapidly digitizing. The pandemic accelerated digital adoption, with 73% of consumers preferring online insurance services and 67% of agents reporting positive responses to digital platforms.
Government Digital Initiatives
- Ayushman Bharat PM-JAY: Over 230 million beneficiaries received Ayushman cards (as of March 2023).
- Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana: Enrolled 313 million beneficiaries.
- Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana: Enrolled 144 million beneficiaries with 600,000+ claims disbursed.
- PMFBY: Paid out $16.7 billion in claims to farmers.
India’s Insurance Market Growth
India is projected to become the 6th largest insurance market by 2032. Key factors driving this growth include:
- Increasing middle-income population (140 million new middle-income households by 2030).
- Growing digital penetration—India is the 2nd largest internet user base, expected to reach 1 billion users by 2026.
- Rising insurance awareness post-COVID.
Conclusion
With strong government backing, digital adoption, and increasing market penetration, India’s insurance industry is poised for exponential growth. Startups like Kshema, a fully digital insurance provider for farmers, are revolutionizing the sector to make financial protection more accessible.
For more details, visit IRDAI or check out the PMFBY official website.