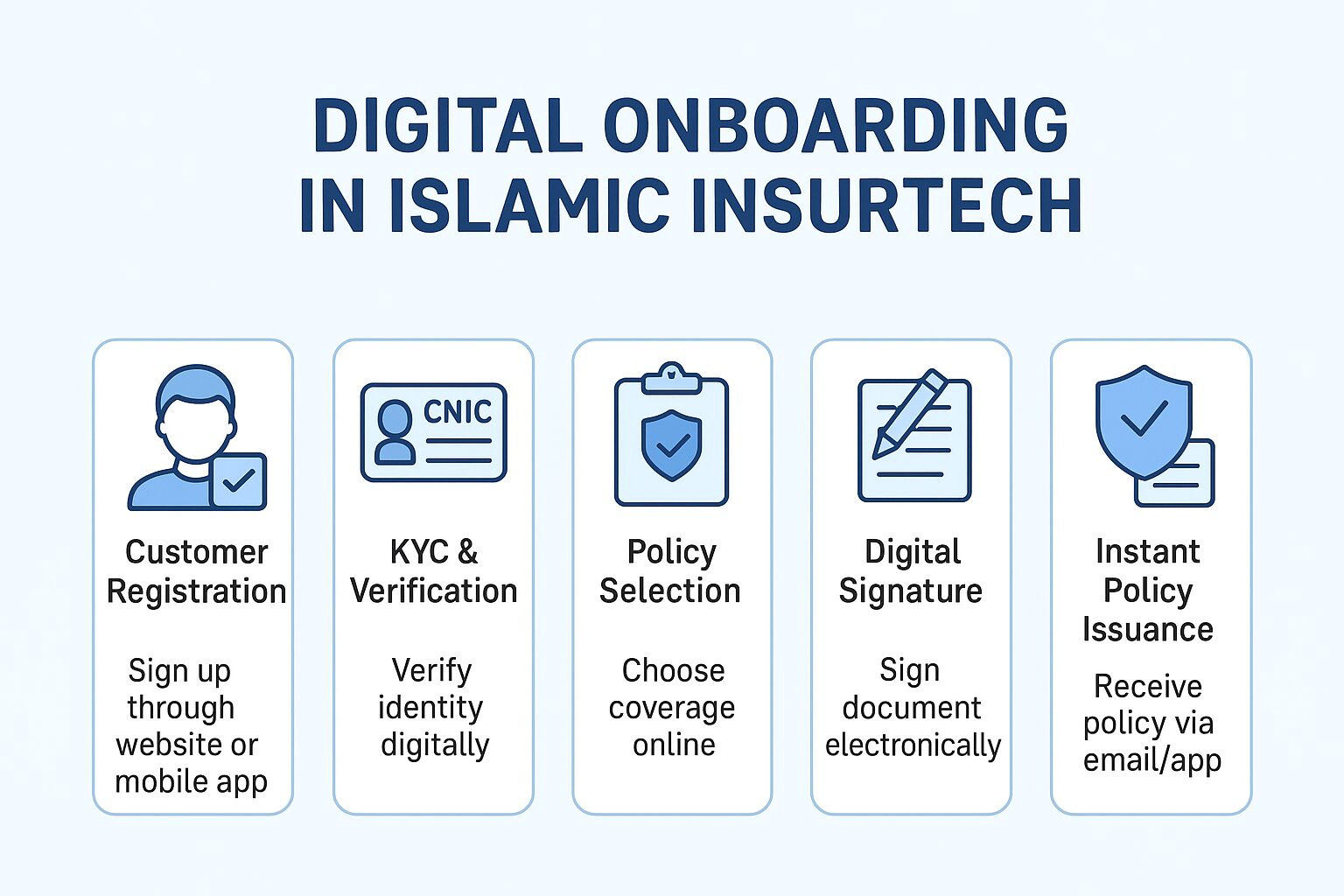
Shariah-Compliant Financial Institutions in Pakistan: Overview, Market Landscape, and Future Potential
1. Introduction
Shariah-compliant finance in Pakistan has grown rapidly over the past two decades, with regulatory support, rising consumer demand for ethical finance, and increasing participation from conventional banks. This report provides a comprehensive overview of the sector, highlighting key players, core principles, product offerings, market size, growth, and future opportunities and challenges.
2. Core Principles of Shariah-Compliant Finance
Shariah-compliant financial institutions operate under Islamic law, emphasizing ethical and risk-sharing principles:
| Principle | Description | Difference from Conventional Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Prohibition of Riba (Interest) | No fixed interest payments; income generated through trade, leasing, or partnerships. | Conventional banks earn interest on loans and deposits. |
| Profit and Loss Sharing (PLS) | Contracts such as Mudarabah (profit-sharing) and Musharakah (joint ventures) distribute profits/losses equitably. | Conventional banks guarantee fixed returns regardless of outcome. |
| Asset-Backed Financing | Transactions must be backed by tangible assets (e.g., house, car, equipment). | Conventional banking can lend money without direct asset-backing. |
| Avoidance of Gharar (Uncertainty) | Contracts must be transparent, clearly stating rights/obligations. | Conventional derivatives and speculative contracts may involve uncertainty. |
| Ethical Investment | Funds cannot be invested in prohibited sectors (alcohol, gambling, interest-based lending, etc.). | Conventional finance does not exclude such sectors. |
3. Market Landscape of Shariah-Compliant Financial Institutions
3.1 Islamic Banking Institutions (IBIs)
| Category | Number / Description |
|---|---|
| Islamic Banking Institutions | ~21 (6 full-fledged Islamic banks + ~15 conventional banks with Islamic banking windows/branches) |
| Branches / Windows | ~6093 branches + ~2651 windows across 132 districts (SBP, 2025) |
3.2 Islamic Microfinance
| Aspect | Detail |
|---|---|
| Number of Branches | 110 Islamic microfinance banking branches (Sept 2024) |
| Major Players | Akhuwat Islamic Microfinance, Naymet, U Bank (Islamic), SAFCO, NRSP Microfinance Bank Limited and U Microfinance Bank Limited |
3.3 Takaful (Islamic Insurance)
| Type | Number / Description |
|---|---|
| General Takaful | 6 full-fledged companies (SBP, 2024) + 20 windows |
| Family Takaful | 3 full-fledged companies + 7 windows |
4. Product Offerings
| Product Type | How It Works | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Deposit & Savings Accounts | Profit-sharing (Mudarabah) instead of interest | Meezan Bank, BOP Taqwa |
| Investment Accounts | Profit/loss sharing pools | HBL Islamic Banking |
| Home Finance | Diminishing Musharakah, Ijarah Muntahia Bittamleek | Meezan Bank Easy Home |
| Auto/Asset Finance | Ijarah or Musharakah-based leasing | Meezan Car Ijarah, Allied Aitebar |
| Trade & Commercial Finance | Murabaha, Salam, Istisna, Running Musharakah | Faysal Bank Islamic |
| Agricultural Finance | Tractor, fish farming, equipment financing | ZTBL Islamic Finance |
| Microfinance/Qard-e-Hasna | Interest-free loans for poor/small entrepreneurs | Akhuwat Islamic Microfinance |
| Digital Banking | Fully digital accounts, payments, debit cards | BankIslami “aik” |
| Takaful | Shariah-compliant insurance products | TPL Insurance, Reliance WTO |
5. Leading Institutions and Their Offerings
| Institution | Category | Key Shariah-Compliant Products |
|---|---|---|
| Meezan Bank | Full-fledged Islamic bank | Current & savings, auto/home finance, trade finance |
| Faysal Bank Islamic | Islamic division | Murabaha, Istisna, Salam, Diminishing Musharakah |
| BankIslami (“aik”) | Fully digital | Digital account opening, instant transfers, debit cards |
| ZTBL | Agricultural bank | Riba-free agricultural finance |
| Akhuwat Islamic Microfinance | Microfinance | Qard-e-Hasna, livelihood loans |
| TPL Insurance / Reliance WTO | Takaful | Auto, health, marine, fire & allied takaful |
6. Market Size & Growth
| Sub-Sector | Market Size / Assets | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Islamic Banking | ~21.1% share of total banking assets (SBP, 2025) | Growing ~17–23% YoY |
| Insurance (Total) | PKR 3.554 trillion (2024) | Takaful ~12% but rising |
| Mutual Funds | PKR 3.93 trillion AUM | Islamic funds ~44% of total |
7. Trends, Opportunities, and Challenges
Islamic Banking: Branch network expanding (~5,000+), deposits growing, market share 19–25%. Opportunities: SME financing, rural expansion, fintech integration. Challenges: Awareness gaps, shortage of skilled staff, higher compliance costs.
Takaful: Growth toward ~35% market share by 2028. Opportunities: Micro-takaful, bundling with banking products. Challenges: Low awareness, limited retakaful capacity, regulatory complexity.
Islamic Microfinance: Growing demand, new branches, fintech integration. Opportunities: Rural financial inclusion, women entrepreneurship. Challenges: Funding constraints, high operating costs, scaling issues.
8. Strengths and Weaknesses
| Aspect | Strengths | Weaknesses / Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Framework | SBP support, AAOIFI adoption, riba-free roadmap | Implementation risk, compliance costs |
| Demand | High from religiously inclined customers, rising corporate demand | Price sensitivity, awareness gap |
| Economic Feasibility | Large banks profitable, sukuk opportunities | Smaller players squeezed, liquidity risks |
9. Future Outlook
The Shariah-compliant finance sector in Pakistan is expected to achieve full riba-free banking by 2027, as mandated by court rulings and supported by SBP initiatives. Growth potential lies in digitalization, rural financial inclusion, SME financing, and product innovation. Takaful and Islamic microfinance are poised to grow rapidly with regulatory support and increased public awareness.
For more articles, Visit Website link: Digital Techno Insurance